| Category 5 severe tropical cyclone (Aus scale) | |
|---|---|
| Category 5 tropical cyclone (SSHWS) | |
 Cyclone Trevor at landfall with a clear eye | |
| Formed | January 29, 2019 |
| Dissipated | February 22, 2019 |
| Highest winds | 10-minute sustained: 270 km/h (165 mph) 1-minute sustained: 305 km/h (190 mph) |
| Lowest pressure | 882 hPa (mbar); 26.05 inHg |
| Fatalities | 453 total, 25 missing |
| Damage | $2.31 billion (2019 USD) |
| Areas affected | Papua New Guinea (Bougainville Island, New Britain, New Ireland, Papuan Peninsula, D'Entrecasteaux Islands), Australia (Queensland, Northern Territory), Solomon Islands |
| Part of the 2018-19 Australian region cyclone season | |
Cyclone Trevor (also known as Severe Tropical Cyclone Trevor) was the most intense Australian tropical cyclone on record, with a minimum barometric pressure of 882 mbar (26.05 inHg) and 10-minute sustained winds of 165 mph (270 km/h). It caused catastrophic damage in entire Carpentaria basin mostly after making landfall there as a strong Category 5 cyclone on the Australian scale. The precursor to Trevor was a tropical low that formed well northeast of Vanuatu on January 29. At 12:00 UTC on January 30, the low developed into a tropical depression. Three days later, it strengthened into a tropical storm. but it became a remnant again, moving to the west, but on February 9, Trevor became a tropical storm some 2,000 kilometers west of the Gulf of Carpentaria, and on February 10 the storm became category 1 and in February 12, it became category 3 on the Fujita scale, touching land in less than six hours later in Heatlands regional park, a generally sparsely populated area, producing about 10 deaths and damages of nearly one billion dollars.When the storm crossed the Cape York and entered in the gulf of the same name as a category 1, Trevor underwent explosive intensification. In a 30-hour period, Trevor's barometric pressure dropped from 984 mbar (29.10 inHg) to 882 mbar (26.04 inHg), and its 10-minute sustained winds increased from 60 mph (95 km/h) to 165 mph (270 km/h). At its peak on the afternoon of February 15, the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) reported that Trevor was an extremely powerful Category 5-equivalent cyclone on the Saffir-Simpson hurricane scale with 1-minute sustained winds of around 190 mph (305 km/h).
Due to land interaction and a moderate westerly wind shear, Trevor began to weaken near landfall. At 18:00 UTC on February 17, it made landfall near Mornington Island, Australia as a strong Category 5 cyclone on the Australian scale.On land Trevor continued to weaken. but an abnormally low rate due for the brown ocean effect over Nicholson area By early on January 18, Trevor had weakened to a Category 1 tropical cyclone,having this category over land for almost 18 hours and near two days as a tropical storm. At around 18:00 UTC on January 21, Trevor degenerated into a remnant low near Wagga Wagga city.
Because of Trevor intensification, residents of Carpentaria Gulf basin. Widespread flooding occurred as a result of a storm surge that reached 30 ft (8.2 m) in some places.In the unpopulated area in the Cape Carpentaria.In Mapoon district,almost the 90% of the buildings and 350 deaths most for the extreme floods.Trevor later caused bad sea conditions and strong rainbands in all Carpentaria Basin.Later in Wellesley and Mornington Islands were reported the worst damages,with the almost 10 per cent of land of these islands disappeared for the erosion and 90 deaths in these islands and surrounded zones.Days later, Trevor's remnants travelled for some unpopulated areas,as a low it produced heavy rainfall in the New South Gales,causing 13 deaths. Overall, as a result of Trevor, 453 people were killed and 25 people were reported missing; as well as this, Trevor caused US$2,31 billion in damage.
Meteorological history[]
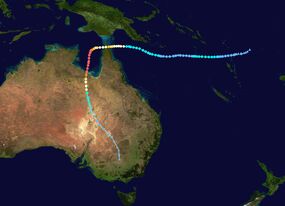
Map plotting the storm's track and intensity, according to the Saffir–Simpson scale
Tropical storm (39–54 mph, 63–87 km/h)
Category 1 (74–95 mph, 119–153 km/h)
Category 2 (96–110 mph, 154–177 km/h)
Category 3 (111–129 mph, 178–208 km/h)
Category 4 (130–156 mph, 209–251 km/h)
Category 5 (≥157 mph, ≥252 km/h)
On January 28, a tropical low formed well northeast of Vanuatu archipelago . For about ten days, the storm moved in an unfavorable environment with a high wind shear, but with fairly hot water, which allowed the circulation of the storm to survive and being named as Trevor, weakening a remnant twice.But when the system was approaching to Louisiade archipelago as a result of it being located within an area of extremely low wind shear and sea surface temperatures of around 88-90 °F (31-32 °C), the system began to intensify relatively quickly. Early on February 10,the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) detected hurricane winds in the storm, reaching category 1 on the Australian scale, Trevor quickly intensified until reaching winds of 115 mph (185 km/h) being classified as a storm of category 3 on the scale of Saffir

Trevor making landfall over Carpentaria Cape
Simpson and category 4 on the Australian scale. Trevor quickly touched down at Heatlands regional park in the far north of Australia, quickly weakening to a category 1 on the Saffir scale.
From February 14 to February 16, Trevor underwent explosive intensification. In approximately 48 hours, Trevor's minimum barometric pressure dropped from 984 mbar (29.15 inHg) to 882 mbar (26.04 inHg) and its 10-minute sustained winds increased from 60 mph (95 km/h) to 190 mph (305 km/h).

Trevor at peak of intensity
During this period, Trevor developed excellent poleward and equatorward outflow and cloud tops of around -145 °F (-99 °C) that wrapped around an eye 25.5 miles (42 kilometers) in diameter. On the evenight of February 16, Trevor reached its peak intensity with a minimum barometric pressure of 882 mbar (26.04 inHg).The measurements made Trevor the strongest Australian region tropical cyclone on record in terms of barometric pressure, 10-minute sustained winds, and 1-minute sustained winds.

Trevor over land as a category 1 cyclone
Shortly after achieving peak intensity,Trevor maintained a pressure under 890 mbar and winds around 300 km/h, The storm turned southward in response to a ridge to its west. By 12:00 UTC on February 17, Trevor still maintain a pressure of 892 mbar and winds of 290 km/h despite of moderate wind shear in it west side,also,the cyclone was reported as a annular cyclone because it features a normal to large, symmetric eye surrounded by a thick and uniform ring of intense convection, having a relative lack of discrete rainbands, and bearing a symmetric appearance in general. Later that day,Trevor made landfall near Mornington Island with 10-minute sustained winds of 250 km/h (155 mph) and a minimum barometric pressure of 896 mbar (26.66 inHg).It began to track inland over the Nicholson region of Central Australia. Despite losing the ocean as its primary source of energy, the cyclone was slow to weaken, partially due to the flat nature of the terrain and possibly also as a result of the brown ocean effect.
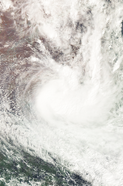
Trevor shortly after being declared as a remnant
The system was only downgraded below tropical cyclone intensity by the BOM after approximately 30 hours over the flat desert of Carpentaria Gulf, at 12:00 pm AWST on 19 February.Gale-force winds did persist in the southeastern quadrant, however, due to the influence of a high-pressure ridge to the southeast of the system. Due to dry air intrusion and high amounts of vertical wind shear, Two days later later, Trevor weakened to a tropical low and began to accelerate southeastward. On February 22, after its low-level circulation center had become entirely devoid of convection, Trevor degenerated into a remnant low while located well south, dissipating in late February 22 near Wagga Wagga city.
Preparations[]
Pacific islands and Papua
At the end of February, Trevor's low precursor crossed near Vanuatu, provoking intense rains and intense winds, but producing minimal damages and no deaths, also rains were produced in the Solomon Islands and Papua, but with few consequences.
Australia
Upon being declared as Tropical Cyclone Trevor again on February 9, the Bureau of Meteorology issued a gale warning for areas along the eastern coast of Far North Queensland. Several hours later, a cyclone warning was issued for north-eastern areas as the storm intensified. An estimated 2,000 people were planned
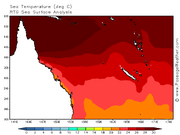
Sea surfaces at 13 February
to be evacuated in Far North Queensland before officials shut down major highways in the area. Ferry services in the Great Barrier Reef and flights in and out of the region were cancelled.However, no evacuations took place according to the Emergency Management in Australia.An aborigine community of 700, located around the mouth of the Lockhart River, were in the direct path of the storm. But not losses were reported in that area,because these people hidden in the accidentated mountains. Strong damage was recorded in Queensland for the rains,but, despite Cyclone Trevor being a Category 3 cyclone, as the storm impacted a sparsely populated region of the Cape York peninsula.A storm surge of 2.23 m (8.0 ft) was recorded
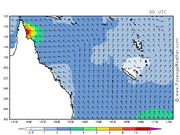
First forecasts indicated a more south storm,which will weakened the storm well more
in Mossman and waves were recorded up to 6.24 m (15.9 ft) in Weipa.Heavy rainfall was also associated with the storm, exceeding the astonishing date of 5512 mm (217 in) near where Trevor made landfall making it the second most wettest tropical cyclone in history. Wind gusts up to 109 km/h (68 mph) were recorded as the storm traversed the peninsula.Officials reported about 90 percent of the structures on most of zones for the catastrophic rains.
Trevor later caused bad sea conditions and strong rainbands in all Carpentaria Basin.Later in Wellesley and Mornington Islands were reported the worst damages,with the almost 10 per cent of land of these islands disappeared for the erosion and 90 deaths in these islands and surrounded zones.Days later, Trevor's remnants travelled for some unpopulated areas,as a low it produced heavy rainfall in the New South Gales,causing 13 deaths.
Impact[]
Australia
Officials closed schools throughout the region in advance of the storm on middle February and advised people to evacuate. A 10 pm curfew was also put in place to keep people off the streets during the night.Local tours in the territory were postponed or cancelled due to the storm. Several flights in and out of Darwin were also cancelled, as was the Darwin Anzac Day march. Alcan, the world's second-largest aluminium producer, warned customers of potential interruptions to supplies on contracts from its Gove refinery.Rio Tinto's Ranger Uranium Mine ceased operations for four days, "for impressive damages".
At one point, Trevor was forecast to pass directly over York. In response, officials evacuated the island's 337 residents to shelters set up in Pine Creek. Numerous schools in the threatened region, especially in Cairns, were closed ahead of Trevor's arrival.Several shelters were opened in Cairns early on February 12 in anticipation of an influx of evacuees. Stores throughout the area reported increased sales for storm supplies, with some reducing prices on specific items.

Damages in Coen city
The Wellesley Islands,located off the coast of the Carpentaria Gulf, suffered significant damage from the storm. Coastal trees were uprooted throughout the islands and sand dunes were destroyed. An outstation located on one of the islands was destroyed by the cyclone.The highest 24-hour rainfall from the storm was recorded near these islands (60 in).
Although the storm made landfall at peak intensity in Australia's Northern Territory, the impacted areas were sparsely populated. Around the region where Trevor made landfall, evidence of a 5–6 m (16.4–19.6 ft) storm surge was present in Junction Bay.
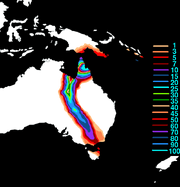
Trevor total rainfall map
Wind gusts up to 148 km/h (92 mph) felled power lines in Maramie and extensive damage was reported in Pieturu. Roughly 10,000 people also lost phone service in the region.Several highways were blocked by fallen trees throughout the area.Damages was estimated in (US$2,31 billion). According to the Northern Territory Insurance Office, structural damage from Cyclone Trevor amounted to A$4 billion (US$3 billion).The remnants of Trevor produced significant rainfall over parts of Queensland and Tasmania,with strong winds.
Aftermath[]
Effects in Australia
Relief efforts in Australia were extensive. The Government of York ordered to provide food for the victims of Trevor,mostly part to the indigenes. Charitable organizations, such as United Way Worldwide, The Task Force for Global Health, and Habitat for Humanity International, raised approximately US$1 billion in donations for people affected by the cyclone.which was inverted in resources and fix the damages.

Soldiers voluntering in damaged zones
Numerous small towns and villages were significantly damaged by Cyclone Trevor. in some all buildings was damaged by the storm. In response to this devastation, several nations and volunteer groups offered to help rebuild houses and businesses there. Germany and France, for example, sent volunteers to the area to rebuild houses that were destroyed by Alu and search for survivors.Also,a lot of volunteers from other parts of Australia helped out with the devastation in York.
Records[]
One of the most notable aspects of Trevor was its intensity. which experienced a barometric pressure drop of 100 millibars in 30 hours. At its peak, Trevor had 10-minute sustained winds of 165 mph (270 km/h), 1-minute sustained winds of 190 mph (305 km/h), and a minimum barometric pressure of 882 mbar (26.04 inHg). This made it the strongest cyclone on record in the Australian region and the southern hemisphere.
Due to its strong associated thunderstorms, Trevor dropped torrential rainfall on much of York Cape, causing landslides and widespread flooding.
Retirement[]
The name Trevor was retired by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO); it was replaced with Argo, which was the first name on TCWC Port Moresby's standby list at the time.
